Keywords: LiFePO4 charging efficiency, temperature impact, lithium battery charge rate, ESS performance
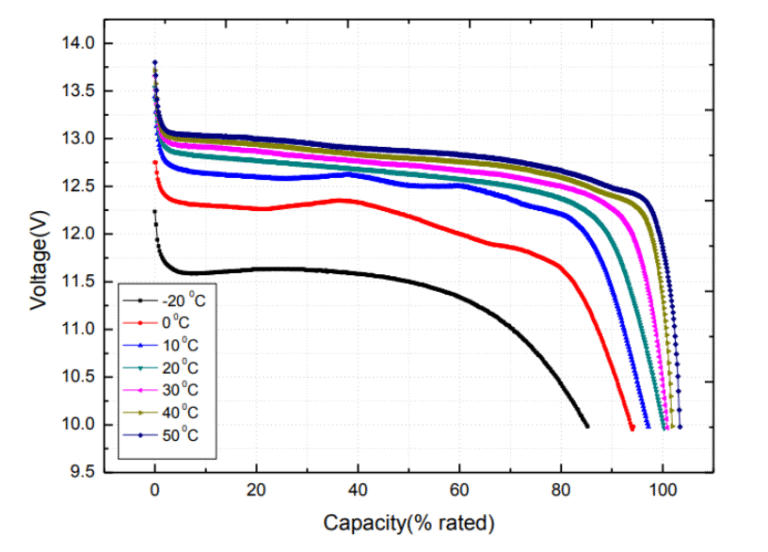
Charging efficiency is highly temperature-dependent. Even with LiFePO₄’s stability, temperature can significantly influence charge speed, current acceptance, and usable energy.
1. High Temperature Charging Behavior
Above 40°C:
- Charge current may be reduced by BMS
- Excess heat accelerates cell aging
- SEI layer grows faster
- Electrolyte oxidation increases
At 50°C, charging efficiency may drop by 20–30%.
2. Low Temperature Charging Behavior
Below 10°C:
- Charge acceptance slows down
- Internal resistance rises
- Charging takes longer
- BMS may reduce charging current
- Below 0°C, charging is disabled (unless heated internally)
3. Why Charging Speed Changes
Temperature affects:
- Lithium ion mobility
- Conductivity of the electrolyte
- Structural stability of the anode
- Voltage thresholds used by BMS
This leads to slower charging in cold and derating in hot climates.
4. Real-World ESS Impact
In solar ESS applications:
- Winter → slower charge from panels
- Summer → heat reduces overall efficiency
- Cloudy days → lower solar + temperature impact
Proper design ensures stable output year-round.
5. The Best Ways to Maintain Charging Efficiency
- Keep battery temperature between 15–30°C
- Allow airflow near charging components
- Use self-heating battery packs in cold regions
- Avoid charging when battery cabinet exceeds 40–45°C
6. Conclusion
Charging efficiency is temperature-sensitive. Proper temperature management ensures the battery can charge quickly and safely across all seasons.